Azure Devops
This guide will show you how to integrate Azure Devops as a CI pipeline with Platformer Console and deploy your containerized applications to an AKS (Azure Kubernetes) Cluster.
Before you begin¶
- You have set up an Organization and a Project on the Platformer Console.
- You have access to Azure Devops and a Kubernetes Cluster (with administrative
kubectlaccess to it). - Assumes basic knowledge of Azure Devops Pipelines, AKS and ACR (and the usage of
azure-pipelines.yamlfiles)
Step 1: Connecting an AKS Cluster to Platformer Console¶
Creating a new AKS Cluster
If you don’t have an AKS Cluster, you can read more about how to set one up here: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/aks/kubernetes-walkthrough-portal
Connect your cluster to the Platformer Console by installing the Platformer Agent. It shouldn’t take more than ~2 minutes to set this up.
Tutorial: Connecting a Cluster to the Platformer Console
Once the cluster has been connected, you should be able to view your Cluster information in the Console.
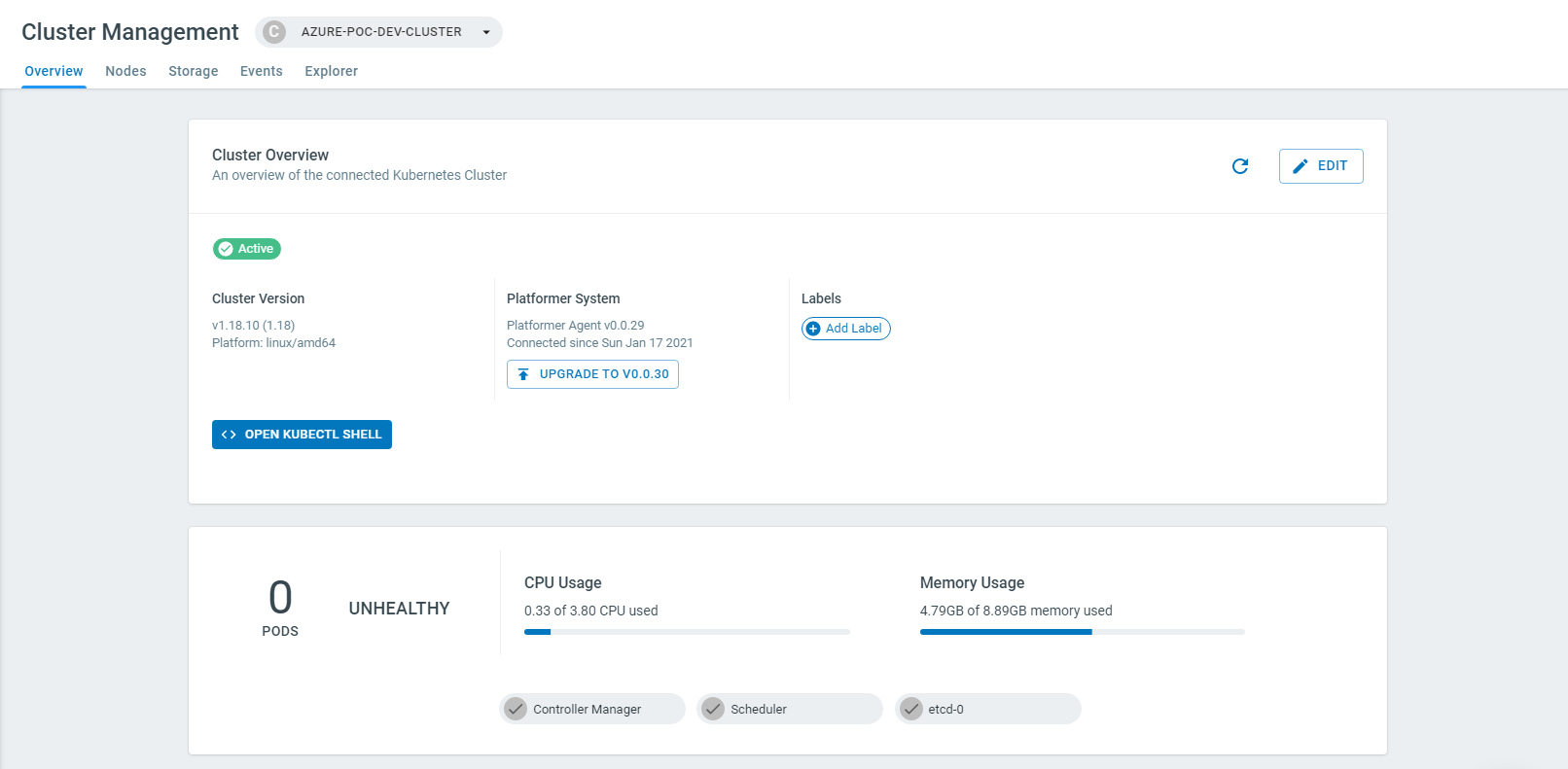
Step 2: Create a new Application¶
Create an Environment
If you don’t have an Environment set up already, follow this article: Creating an Environment
To create a new Application, go to Applications > Create and select the Simple Application Setup and follow the set up wizard to completion.
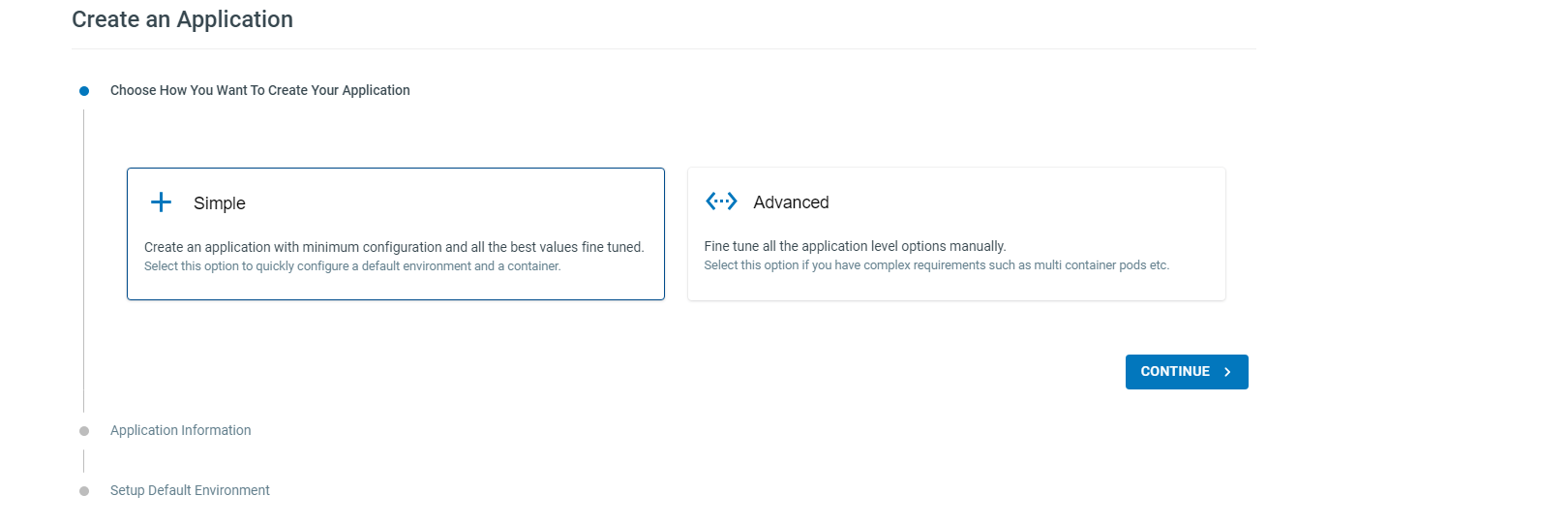
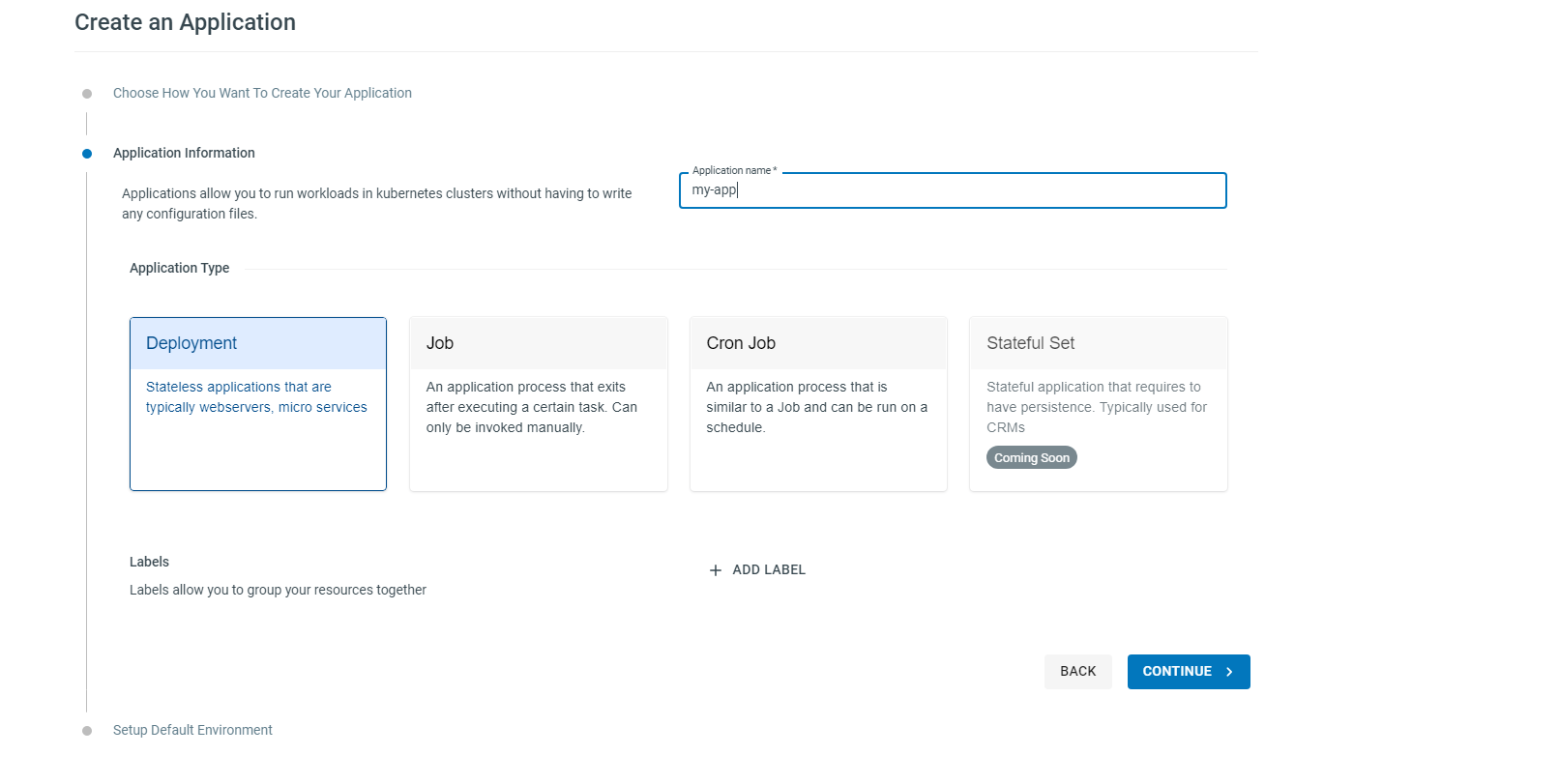
Select the Deployment type, and give your application a name.
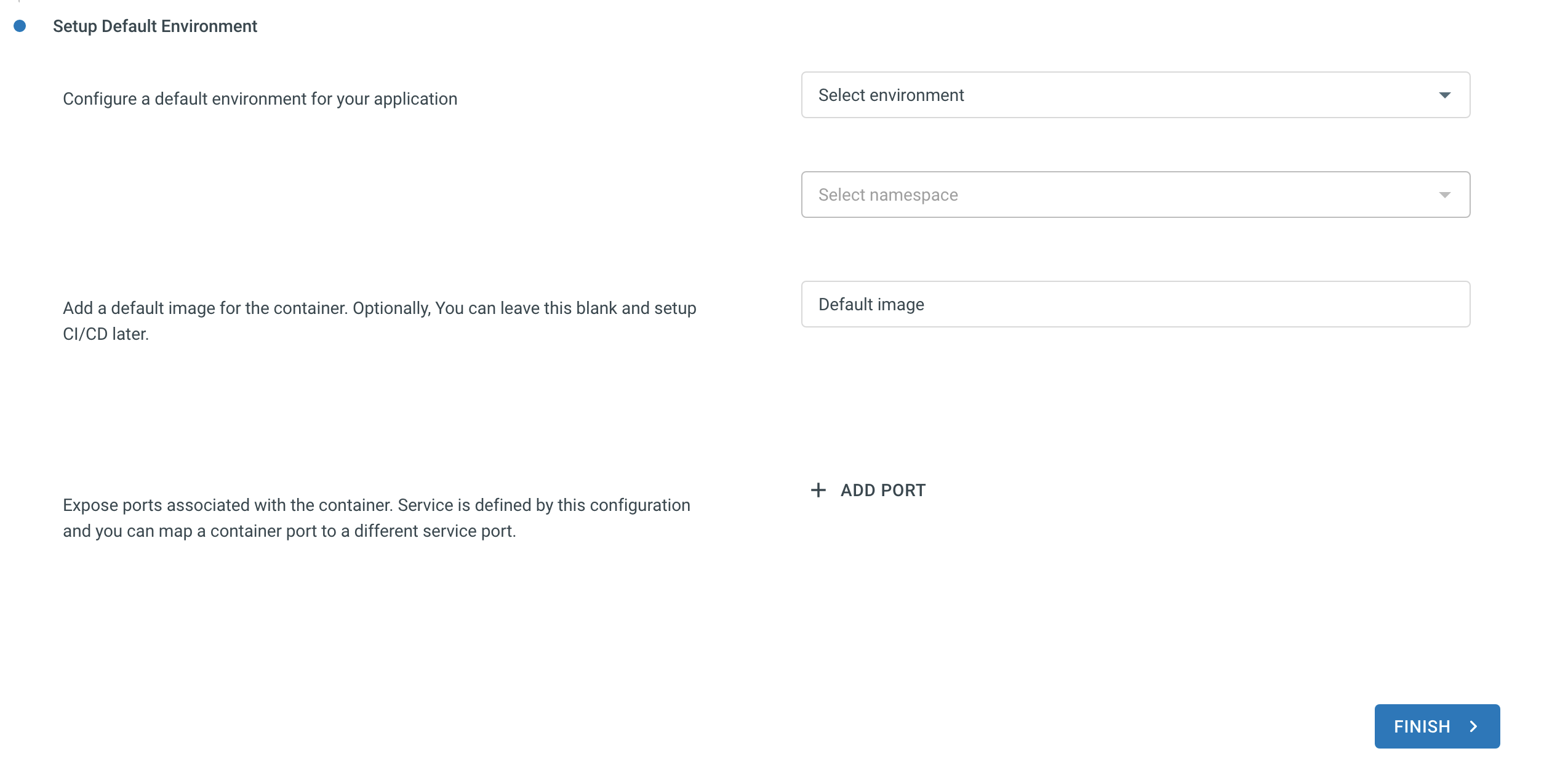
Select the Environment and a namespace.
You don’t have to fill the default image section as we will be using azure deveops to build and deploy new images later in this tutorial.
Add Ports if your container exposes any.
Step 3: Azure DevOps Pipelines¶
Now that our first Application is scaffolded, we can switch back to setting things up on Azure.
Prerequisite 1: Set up an Azure Container Registry
Create an Azure Container Registry for your application. Read more
Prerequisite 2: Integrate AKS with ACR (Allow the Kubernetes Cluster to access the Container Registry)
This can be done in two ways:
- Directly via Azure - Read more
- Through the Platformer Console using Container Registry Integrations - Learn how to integrate ACR with Plaformer Console
Go to Applications > [ Your App ] > Webhooks (tab) and select Azure DevOps Pipelines from the top-right dropdown.
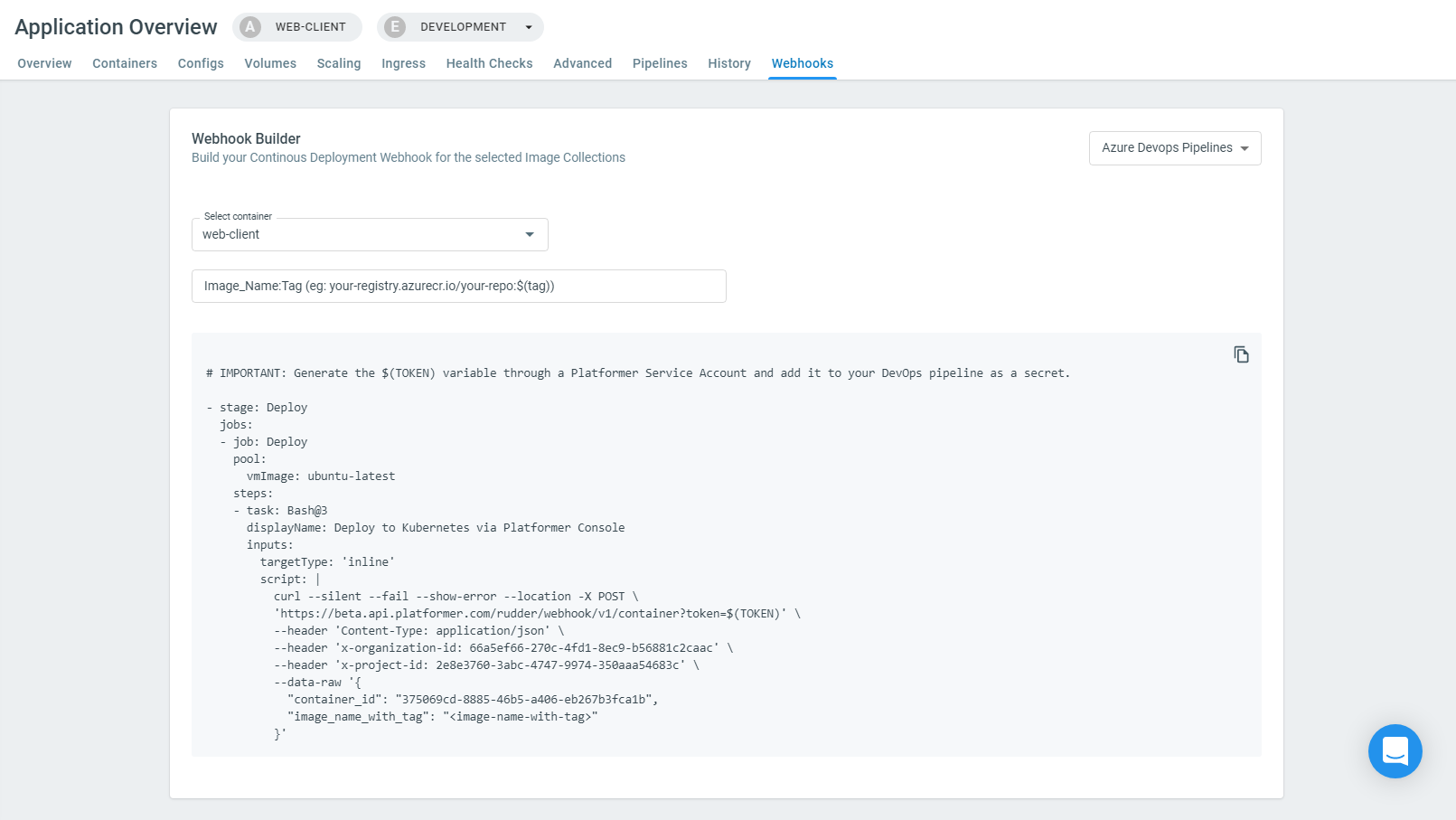
We can now use the generated YAML snippet in your azure-pipelines.yaml to build and deploy the application.
The following YAML outlines a common azure-pipelines configuration. If you already have an existing pipeline config, you only need to append the Deploy stage to it.
The following snippet uses a
Variable Group (in Azure Devops)to store the following values (this is completely optional)
PL_TOKEN: Platformer Service Account Token. Learn how to create a Service Account TokenPL_ORGANIZATION: Platformer Organization ID (copied from the webhooks tab)PL_PROJECT: Platformer Project ID (copied from the webhooks tab)
trigger:
- main
- master
resources:
- repo: self
variables:
# Optional variable group: Contains PL_ORGANIZATION, PL_PROJECT and PL_TOKEN
- group: platformer-console
# These values represet a common configuration. Modify them as required.
- name: dockerRegistryServiceConnection
value: '' # ACR serivce connection string
- name: containerRegistry
value: 'your-repo.azurecr.io' # Your ACR Name
- name: tag
value: '$(Build.BuildId)'
- name: vmImageName
value: 'ubuntu-18.04'
stages:
- stage: Build
jobs:
- job: Build
displayName: Build my-app Image
pool:
vmImage: $(vmImageName)
steps:
- task: Docker@2
displayName: Build and push the image to ACR
inputs:
# Modify as required
command: buildAndPush
# repository: ''
# buildContext: '.'
# dockerfile: $(Build.SourcesDirectory)/Dockerfile
containerRegistry: $(dockerRegistryServiceConnection)
tags: |
$(tag)
# Copy the snippet generated from the Webhooks tab below
# Update the values as required
- stage: Deploy
jobs:
- job: Deploy
displayName: Deploy to AKS via Platformer
pool:
vmImage: $(vmImageName)
steps:
- task: Bash@3
displayName: Deploy my-app via Platformer Console
inputs:
targetType: 'inline'
script: |
curl --silent --fail --show-error --location -X POST \
'https://api.platformer.com/rudder/webhook/v1/container?token=$(PL_TOKEN)' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'x-organization-id: $(PL_ORGANIZATION)' \
--header 'x-project-id: $(PL_PROJECT)' \
--data-raw '{
"container_id": "< Copy from Console >",
"image_name_with_tag": "< Eg. my-app.azurecr.io/my-app:$(tag) >"
}'
Step 4: Deploy¶
Once the azure-pipelines.yaml has been modified and added to the root of your Git repository, the application will be deployed to your Environment via the Platformer Console the next time you make a push to any of the trigger branches.
Next steps¶
Learn how to add configuration files, secrets, etc here: Configurations and Secrets.
Refer to the other articles in the User Guide to learn more about workload management on the Platformer Console.